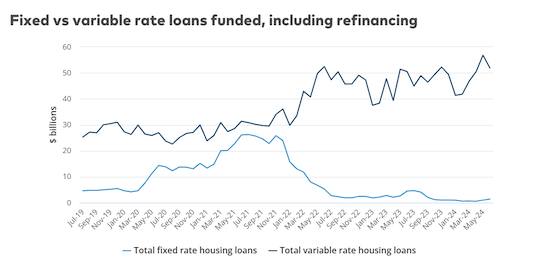
The funding gap between variable and fixed rate loans is continuing to widen.

.
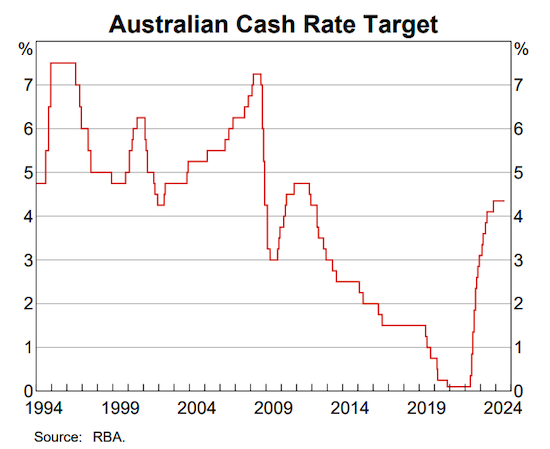
Reserve Bank of Australia governor, Michelle Bullock, was abundantly clear last week when she told attendees at a media briefing they should not expect any cuts to interest rates within the next six months.
The briefing followed the RBA’s monetary policy decision to keep its cash rate on hold at 4.35% for a sixth straight month.
Citing still-high inflation, Bullock said that while the market has been pricing in interest rate reductions by the end of this year, a near-term reduction in the current cash rate doesn’t align with the RBA board’s current thinking.
“Make no mistake, inflation is still too high and the board does remain concerned about the degree of excess demand in the economy,” she said. “If it does appear that inflation is not tracking the way we are forecasting then they will, if needed, increase interest rates.”
It’s very clear that the RBA’s policy tightening has markedly weakened growth and is having a large effect on some households.
— Grant Feng,
Vanguard Senior Economist
Borrowers are banking on rates relief
The average interest rate on a standard variable residential property mortgage with a 70-80% loan-to-valuation ratio is now around 6.25%, with some mortgage products closer to 7%.
Fixed rate property loans, ranging from one to five-year terms, are broadly in the same rates band.
Yet data released by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority, which oversees banks and other mortgage lenders, shows that home loan borrowers have been steadily moving away from taking out fixed rate loans since the RBA began raising interest rates.
When Australian interest rates were cut to record lows over 2020 and 2021 the split between borrowers taking out variable rate home loans over fixed rate loans was fairly narrow.
In June 2021, for example, the APRA data shows $26.1 billion was borrowed using fixed rate mortgages versus $31.4 billion using variable rate mortgages, a gap of just over $5 billion.
That compared with June 2024, when around $1.4 billion was borrowed through fixed rate loan facilities versus $51.9 billion via variable rate mortgages.
Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics
The growing gap between the use of fixed and variable rate mortgages suggests many borrowers are reluctant to lock in their mortgage at the current higher rate levels on the expectation the RBA will start moving rates down again over the shorter term.
To lock in at current levels could leave some borrowers paying substantially higher repayments than those on variable rates once they begin falling.
Yet, how soon that actually happens is an open question, and there’s still a possibility the RBA may raise rates.
Sticky inflation keeps rates on hold
Vanguard Senior Economist, Grant Feng, says the RBA’s decision to keep rates on hold this month signals that rate cuts are off the agenda for the foreseeable future.
“Vanguard expects the RBA to remain on hold throughout this year, before it commences a gradual easing cycle alongside a weakening in both inflation and the labour market,” Feng says.
“As we saw with the release of the latest CPI data, inflation levels are still very sticky, which is why the central bank is embracing a higher-for-longer rates trajectory.
“It’s very clear that the RBA’s policy tightening has markedly weakened growth and is having a large effect on some households. Growth in the economy has almost stalled, led by a weakening in consumer spending.
“However, on the supply side, unit labour costs have continued to rise at a rate that’s above the level consistent with reaching the RBA’s 2-3% inflation target.”
Governor Bullock noted that the RBA board did consider a rate rise at its latest meeting, as well as a hold.
“The judgement of the board was keeping the interest rate where it is, and making sure that people understand that a rate cut is not on the agenda in the near term, given what we know.
“The likelihood of a rate rise hasn’t increased. The board are remaining vigilant to the risks that getting back to target [on inflation] will continue to shift out.”
Important information
This article contains certain 'forward looking' statements. Forward looking statements, opinions and estimates provided in this article are based on assumptions and contingencies which are subject to change without notice, as are statements about market and industry trends, which are based on interpretations of current market conditions. Forward-looking statements including projections, indications or guidance on future earnings or financial position and estimates are provided as a general guide only and should not be relied upon as an indication or guarantee of future performance. There can be no assurance that actual outcomes will not differ materially from these statements. To the full extent permitted by law, Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd (ABN 72 072 881 086 AFSL 227263) and its directors, officers, employees, advisers, agents and intermediaries disclaim any obligation or undertaking to release any updates or revisions to the information to reflect any change in expectations or assumptions.
© 2024 Vanguard Investments Australia Ltd. All rights reserved.
Tony Kaye
August 24
vanguard.com.au